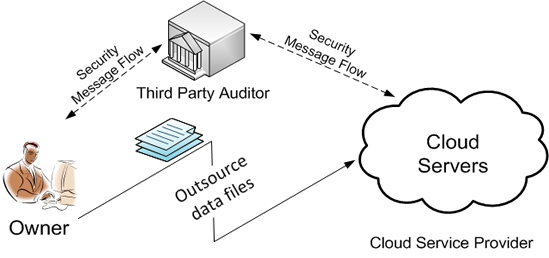
Cong Wang, Sherman S.M. Chow, Qian Wang, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Privacy-Preserving Public Auditing for Secure Cloud Storage," IEEE Transactions on Computers (TC), 2011 (A preliminary version of this paper appeared at the 29th IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM'10)).
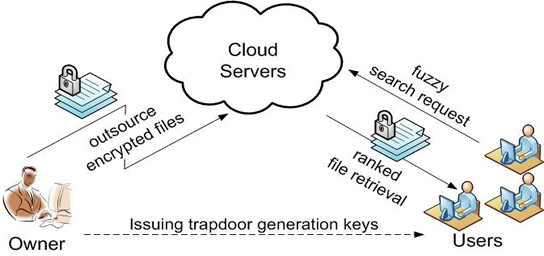
Cong Wang, Ning Cao, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Enabling Secure and Efficient Ranked Keyword Search over Outsourced Cloud Data," IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems (TPDS), 2011 (A preliminary version of this paper appeared at the 30th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS'10)).
Qian Wang, Cong Wang, Kui Ren, Wenjing Lou, and Jin Li, "Enabling Public Verifiability and Data Dynamics for Storage Security in Cloud Computing", To appear, IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems (TPDS), Vol. 22, No. 5, pp. 847-859, May, 2011. (A preliminary version of this paper appeared at the 14th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS'09).)
Cong Wang, Qian Wang, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Towards Secure and Dependable Storage Services in Cloud Computing," To appear, IEEE Transactions on Service Computing (TSC). (A preliminary version of this paper appeared at the 17th IEEE International Workshop on Quality of Service (IWQoS'09)).
Cong Wang, Kui Ren, Shucheng Yu, and Karthik Mahendra Raje Urs, "Achieving Usable and Privacy-assured Similarity Search over Outsourced Cloud Data", IEEE INFOCOM'12, Orlando, Florida, March 25-30, 2012
Cong Wang, Kui Ren, Jia Wang, and Karthik Mahendra Raje Urs, "Harnessing the Cloud for Securely Solving Large Systems of Linear Equations,"
The 31st International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS'11), Minneapolis, MN, June 20-24, 2011. (Note: this online version is the extended full paper of the conference camera-ready one.)
Ning Cao, Zhenyu Yang, Cong Wang, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Privacy-perserving Query over Encrypted Graph-Structured Data in Cloud Computing," The 31st International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS'11), Minneapolis, MN, June 20-24, 2011.
-
Cong Wang, Kui Ren, and Jia Wang,
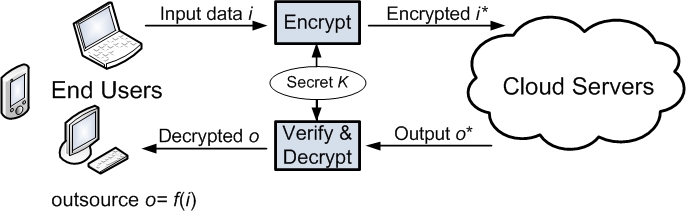
"Secure and Practical Outsourcing of Linear Programming in Cloud Computing",
The 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM'11), Shanghai, China, April 10-15, 2011. (Note: this online version is the extended full paper of the conference camera-ready one.)
Ning Cao, Cong Wang, Ming Li, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Privacy-Preserving Multi-keyword Ranked Search over Encrypted Cloud Data", The 30th IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM'11), Shanghai, China, April 10-15, 2011.
Cong Wang, Kui Ren, Wenjing Lou, and Jin Li, "Towards Publicly Auditable Secure Cloud Data Storage Services", IEEE Network Magazine, Vol. 24, No. 4, pp. 19-24, July/August 2010
Cong Wang, Ning Cao, Jin Li, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Secure Ranked Keyword Search over Encrypted Cloud Data", The 30th International Conference on Distributed Computing Systems (ICDCS'10), Genoa, Italy, June, 21-25, 2010.
Shucheng Yu, Cong Wang, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Attribute Based Data Sharing with Attribute Revocation", The 5th ACM Symposium on Information, Computer and Communications Security (ASIACCS'10), Beijing, China, April 13-16, 2010.
Cong Wang, Qian Wang, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Privacy-preserving Public Auditing for Data Storage Security in Cloud Computing", The 29th IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM'10), San Diego, CA, March 15-19, 2010.
Shucheng Yu, Cong Wang, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Achieving Secure, Scalable, and Fine-grained Data Dccess Control in Cloud Computing", The 29th IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM'10), San Diego, CA, March 15-19, 2010.
Jin Li, Qian Wang, CongWang, Ning Cao, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Fuzzy Keyword Search over Encrypted Data in Cloud Computing", The 29th IEEE Conference on Computer Communications (INFOCOM'10), mini-conference, San Diego, CA, March 15-19, 2010.
Qian Wang, Cong Wang, Jin Li, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Enabling Public Verifiability and Data Dynamics for Storage Security in Cloud Computing", The 14th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security (ESORICS'09), Saint Malo, France, September 21-23, 2009.
Shucheng Yu, Kui Ren, Wenjing Lou, and Jin Li, "Defending Against Key Abuse Attacks in KP-ABE Enabled Broadcast Systems", The 5th International Conference on Security and Privacy in Communication Networks (Securecomm'09), Athens, Greece, Sept. 14-18, 2009.
Cong Wang, Qian Wang, Kui Ren, and Wenjing Lou, "Ensuring Data Storage Security in Cloud Computing", The 17th IEEE International Workshop on Quality of Service (IWQoS'09), Charleston, South Carolina, July 13-15, 2009.